
Ling Xu became Grain in Beard, and the peasant family cut in the sky.
The branch is full, stop watching the movie.
-- "farming Picture 23, its Ten transplanting Seedling," Qing Yin Ying
Grain in Beard is the third solar term in summer.It is also known as "busy planting" and is of great significance in farming. After solar terms, the temperature begins to rise significantly and the rainfall is abundant, which is suitable for planting cereal crops such as late rice. This is the truth embodied in the folk proverb "Grain in Beard does not plant, then he will plant useless".
The popular science of solar terms will be introduced to you.The relationship between intestinal microorganisms and obesity.
The human body is a huge library of microflora, which can be found in all organs of the human body. AndIntestinal tractIt is one of the largest microbial communities in the human body.
The gastrointestinal tract of adults is home to about 1000 species of bacteria, with a total of up to1014Its number is even more than that of human body cells!
What are the main microorganisms in the human intestinal tract?
Bacteria
At the gate level, the two most abundant phyla are Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes, which together constitute more than 80% of intestinal microorganisms.
Thick-walled bacteria can decompose cellulose in the intestinal tract and improve the utilization efficiency of organic matter in the human body. Bacteroides can regulate the balance of intestinal flora.
In addition, it also includes Proteus (Proteobacteria), actinomycetes (Actinobacteria), verruca (Verrucomicrobia), Clostridium (Fusobacteria) and so on.
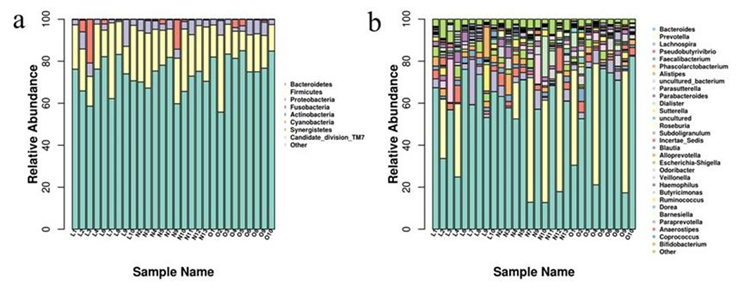
Fig. 1 (a) species abundance of intestinal flora at phyla level; (b) species abundance of intestinal flora at genus level
Photo Source: Lu Yanrong. Study on the relationship between intestinal microorganisms and human energy balance and endocrine and metabolic diseases [D]. Lanzhou. Lanzhou University, 2021.
Fungus
The fungi in the intestinal tract are mainly yeasts, including Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans, which can help the human body digest substances such as glucose and lactose.
In addition, Trichoderma is also one of the common fungi in the human intestinal tract, which can decompose substances such as lignocellulose and cellulose. The number of Aspergillus flavus in the intestinal tract is relatively small, but it has a great impact on human intestinal health, and may lead to intestinal mucosal inflammation and toxin growth.
Virus
The most common viruses in the intestines are coronaviruses and adenoviruses. In addition, there are many other kinds of viruses in the intestinal tract, all of which may cause human intestinal infection.
However, in a healthy state, the number of viruses in the intestinal microbial community is relatively small, and generally rely on the body's immune system to suppress the virus.
A variety of microorganisms and their metabolites in the human intestinal tract play a very important regulatory role in the life process of the host, including substance and energy metabolism, maintenance of intestinal mucosal barrier, regulation of immune function and so on.
It is generally believed that the main causes of obesity are increased energy intake and lack of physical activity. In fact, obesity has been shown to be a complex condition.
In recent years, a large number of experiments have shown that the change of intestinal flora is also one of the influencing factors to promote obesity and metabolic disorders.
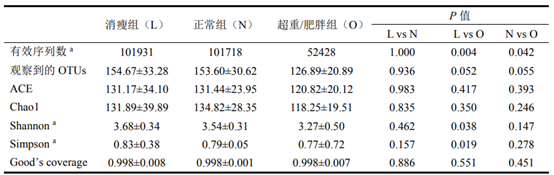
Table 1 comparison of richness and diversity of intestinal microorganisms among different stature groups
Epigenetic source: "study on the relationship between intestinal microorganisms and human energy balance and endocrine and metabolic diseases"
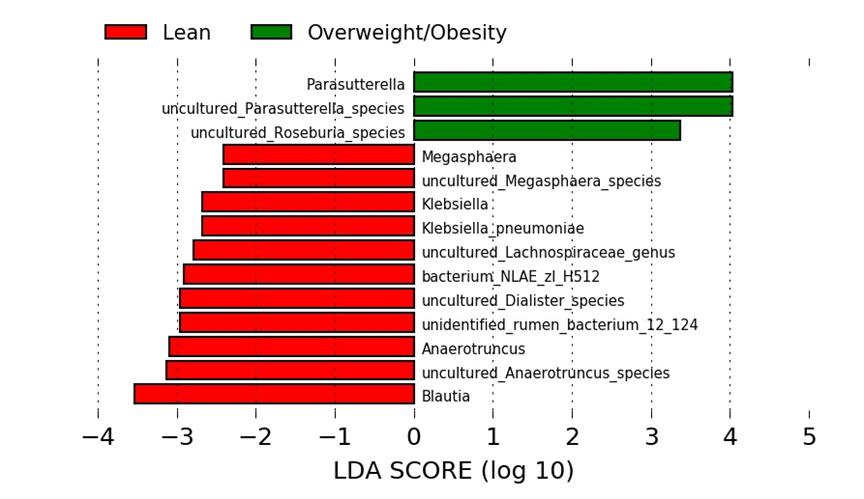
Fig. 2 LEfSe analysis of characteristic differences between weight loss group and overweight / obesity group
Epigenetic source: "study on the relationship between intestinal microorganisms and human energy balance and endocrine and metabolic diseases"

The relationship and mechanism between intestinal flora and obesity
1
Intestinal microflora can produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) by fermenting dietary fiber, proteins and peptides in the colon, thus promoting energy absorption and metabolism. A wide variety of SCFAs, including acetate, propionate and butyrate, have been shown to play a useful role in controlling the occurrence and development of obesity and maintaining glucose homeostasis.
2
Intestinal microorganisms are closely related to immune status and inflammatory response. Obesity and metabolic disorders are often accompanied by chronic low-grade inflammation of the whole body and adipose tissue. Intestinal microecological disorders may lead to increased intestinal permeability and chronic low-grade inflammation, resulting in the increase of adipose tissue.
3
Intestinal flora may also regulate human metabolism through the intestinal endocrine system. It has been proved that intestinal flora can regulate the level of GLP-1 (glucagon-likepeptide 1) secreted by rats. Hormones such as GLP-1 can slow down gastric emptying, induce insulin release and increase satiety.
There are many kinds of intestinal microorganisms, and there are complex interactions between them. The study of intestinal microorganisms is not only very important for human health, but also has reference significance for the effective prevention and treatment of related diseases in clinical medicine.

"24 solar terms" for microbial targeted prevention and controlIt is a new popular science column on microbial prevention and control launched by Hanning Chemical in 2022. We will regularly launch popular science essays on microbial prevention and control on the Chinese traditional 24 solar terms."the four seasons are orderly, everything is sometimes", let's "send knowledge in the season"To explore the microbial world together:Hanning will make an appointment with you at the right time.
